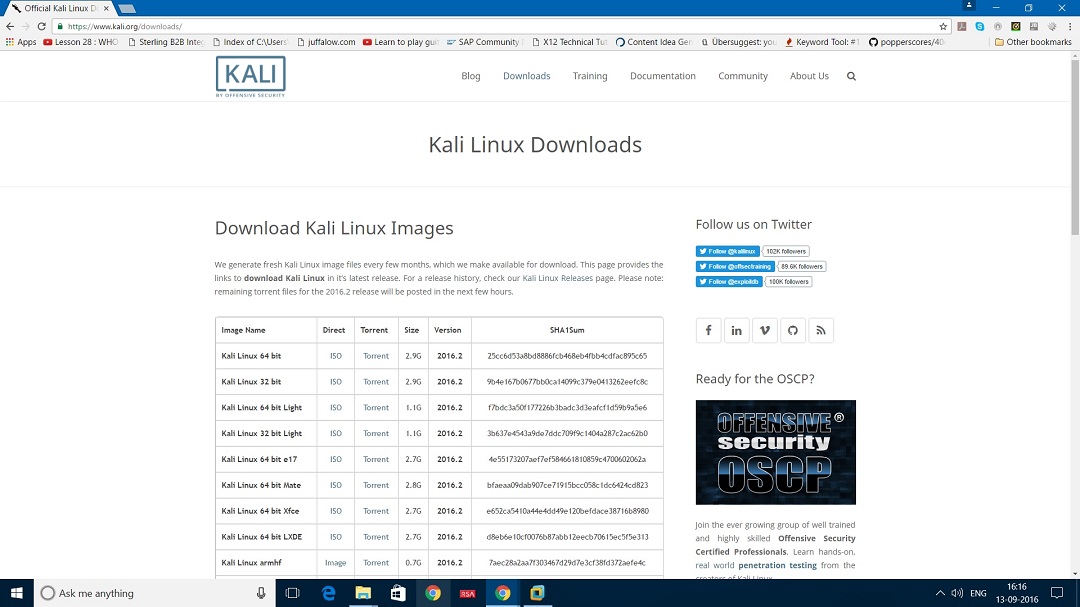
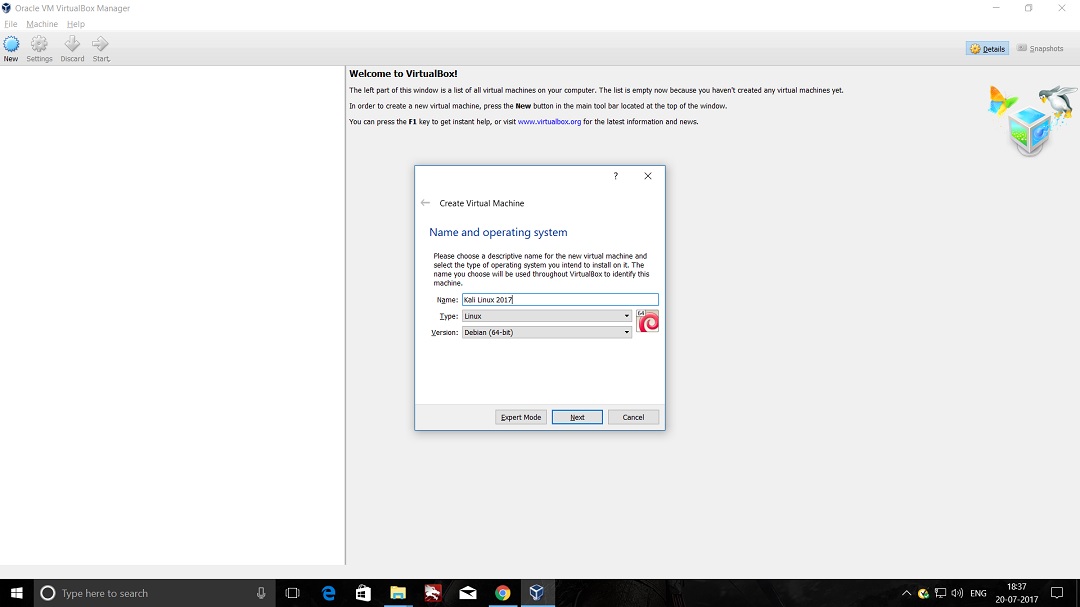
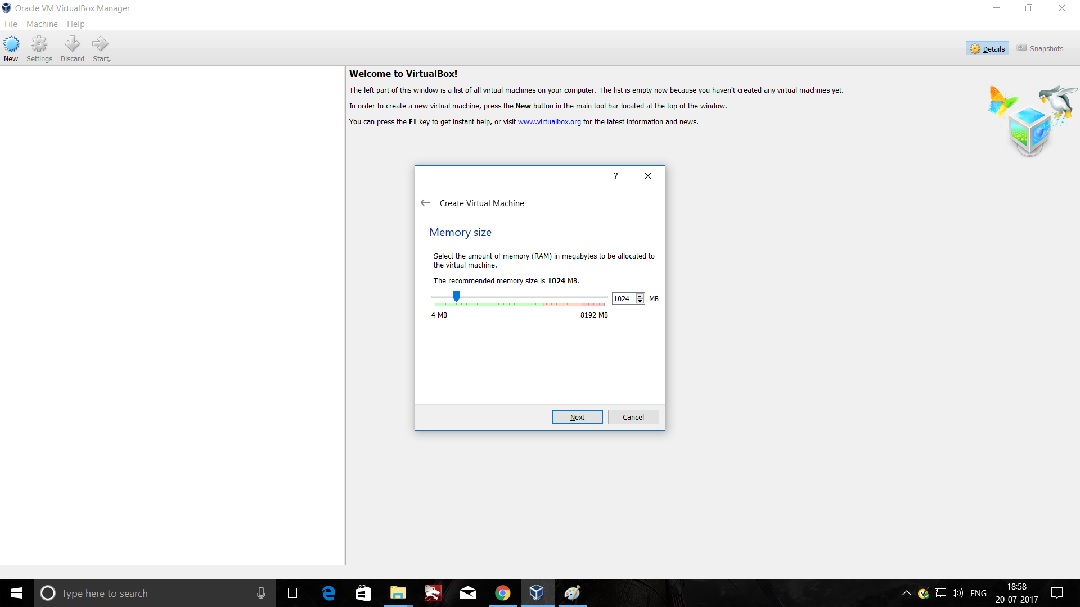
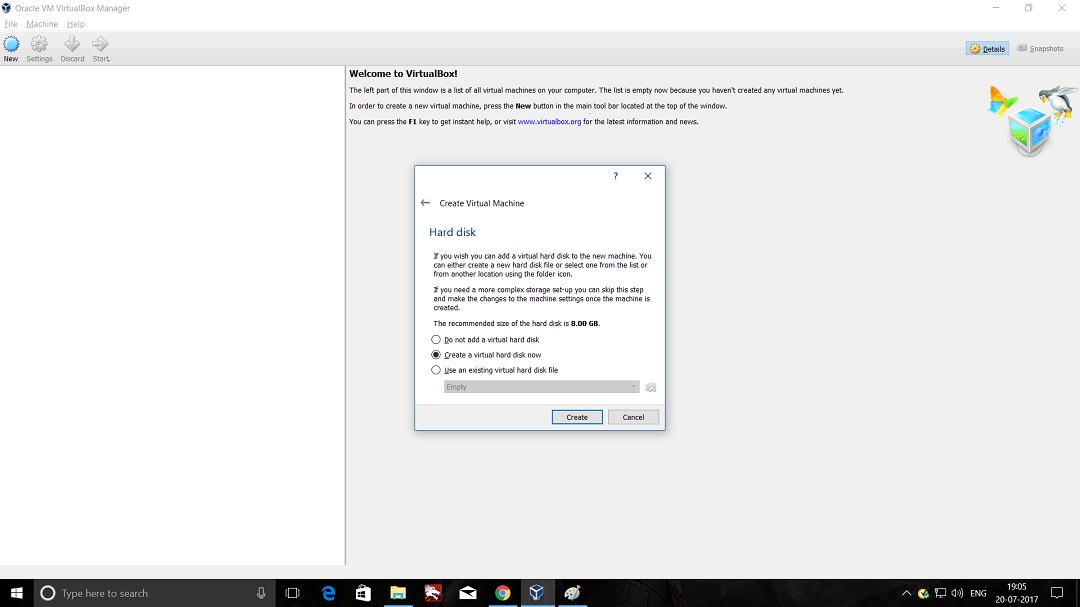
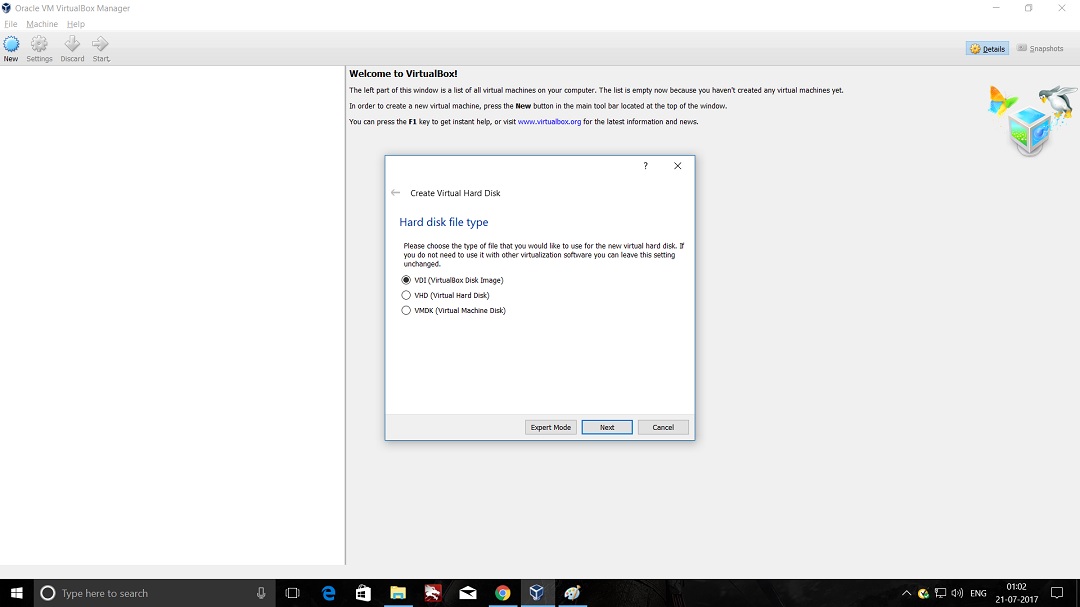
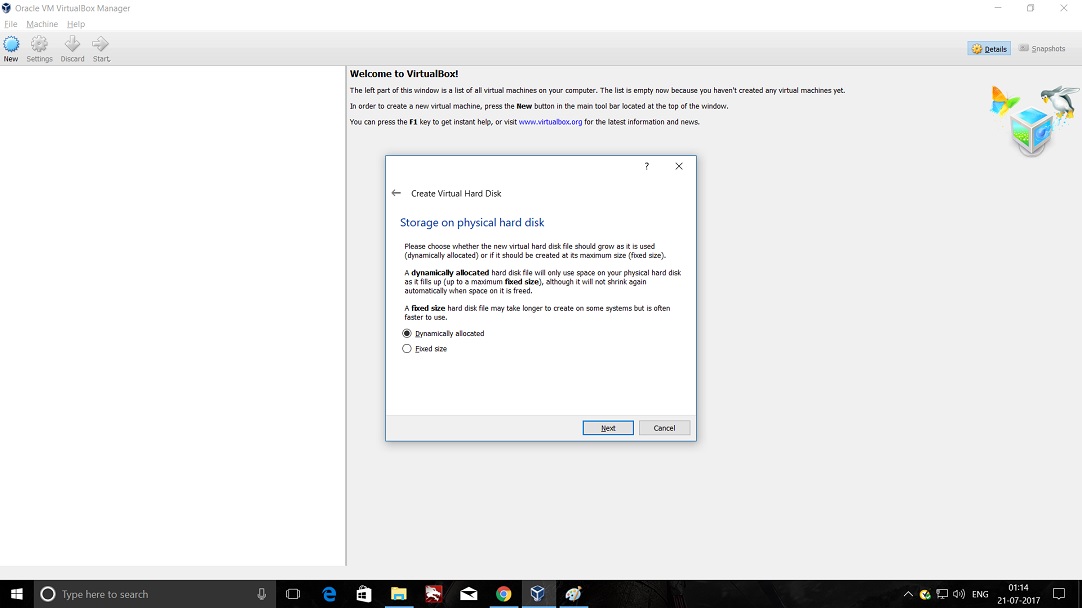
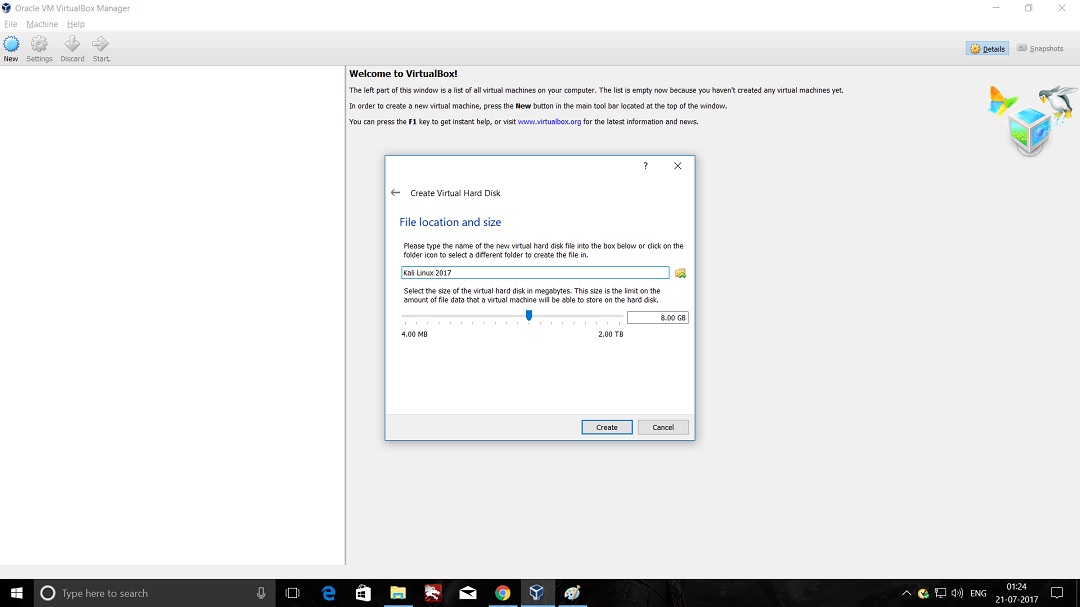
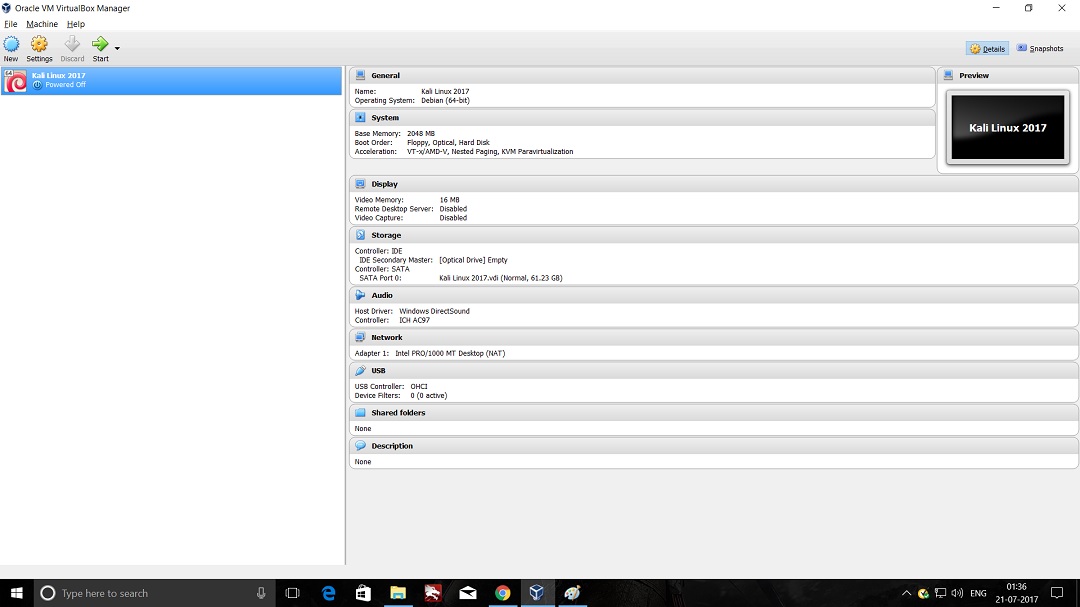
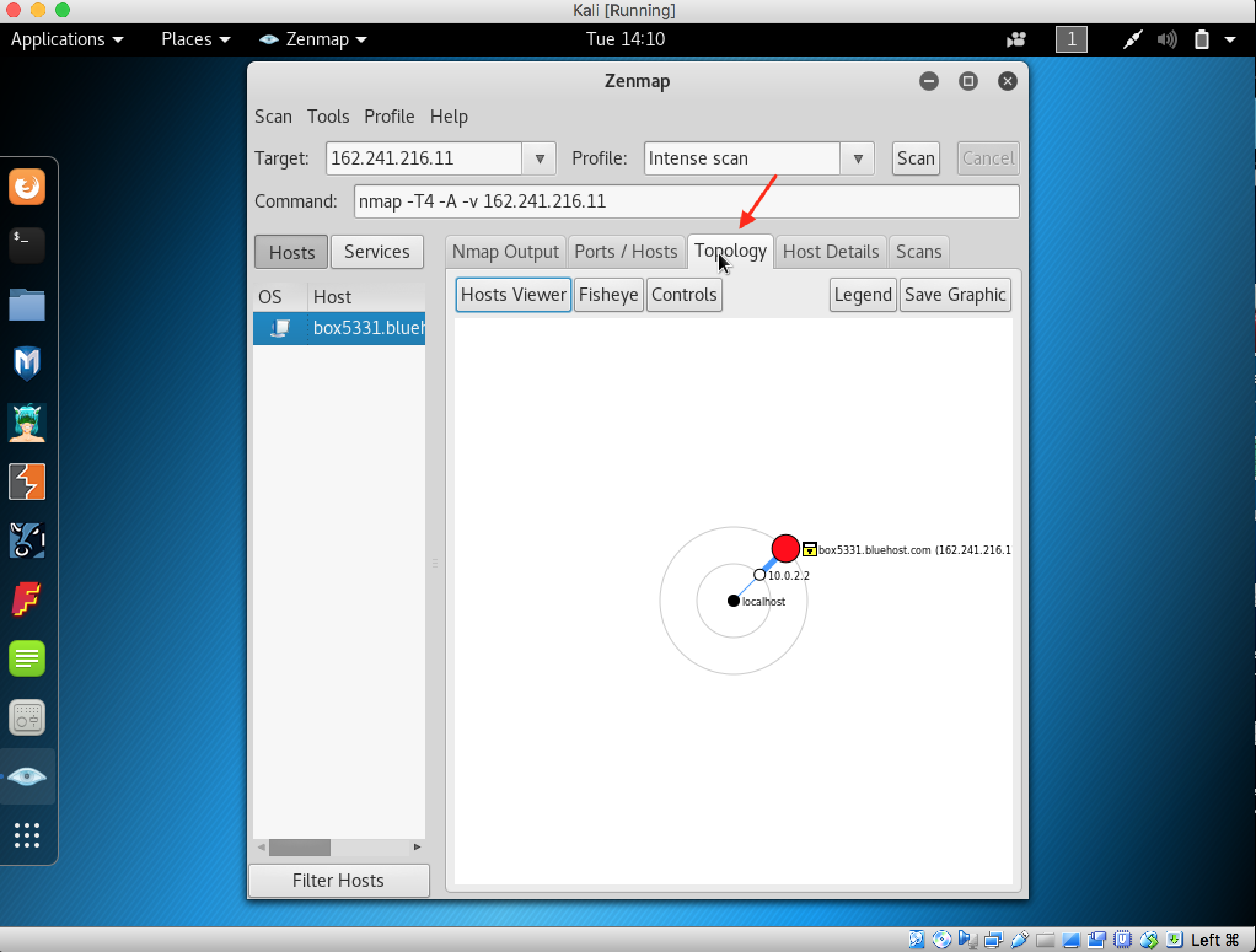
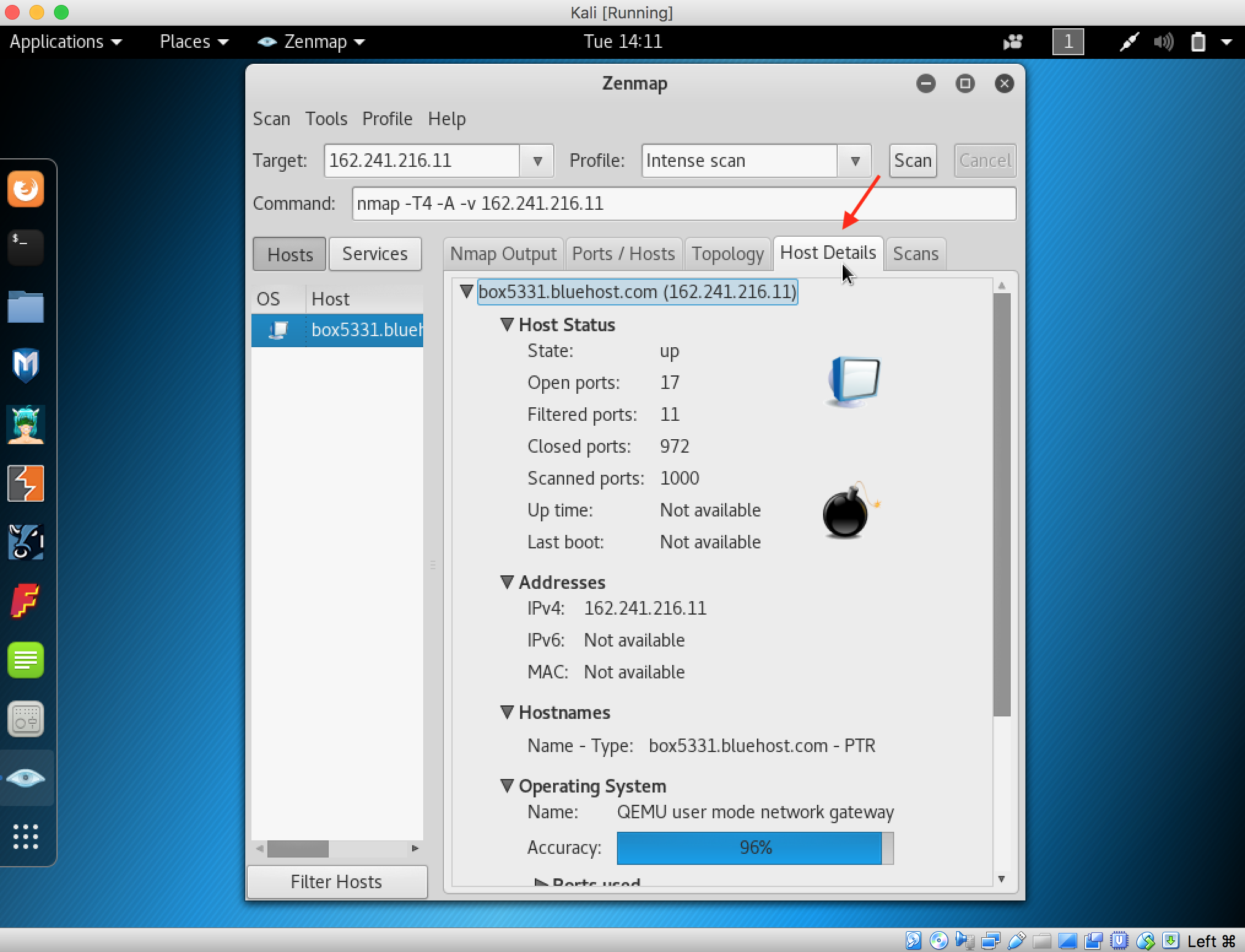
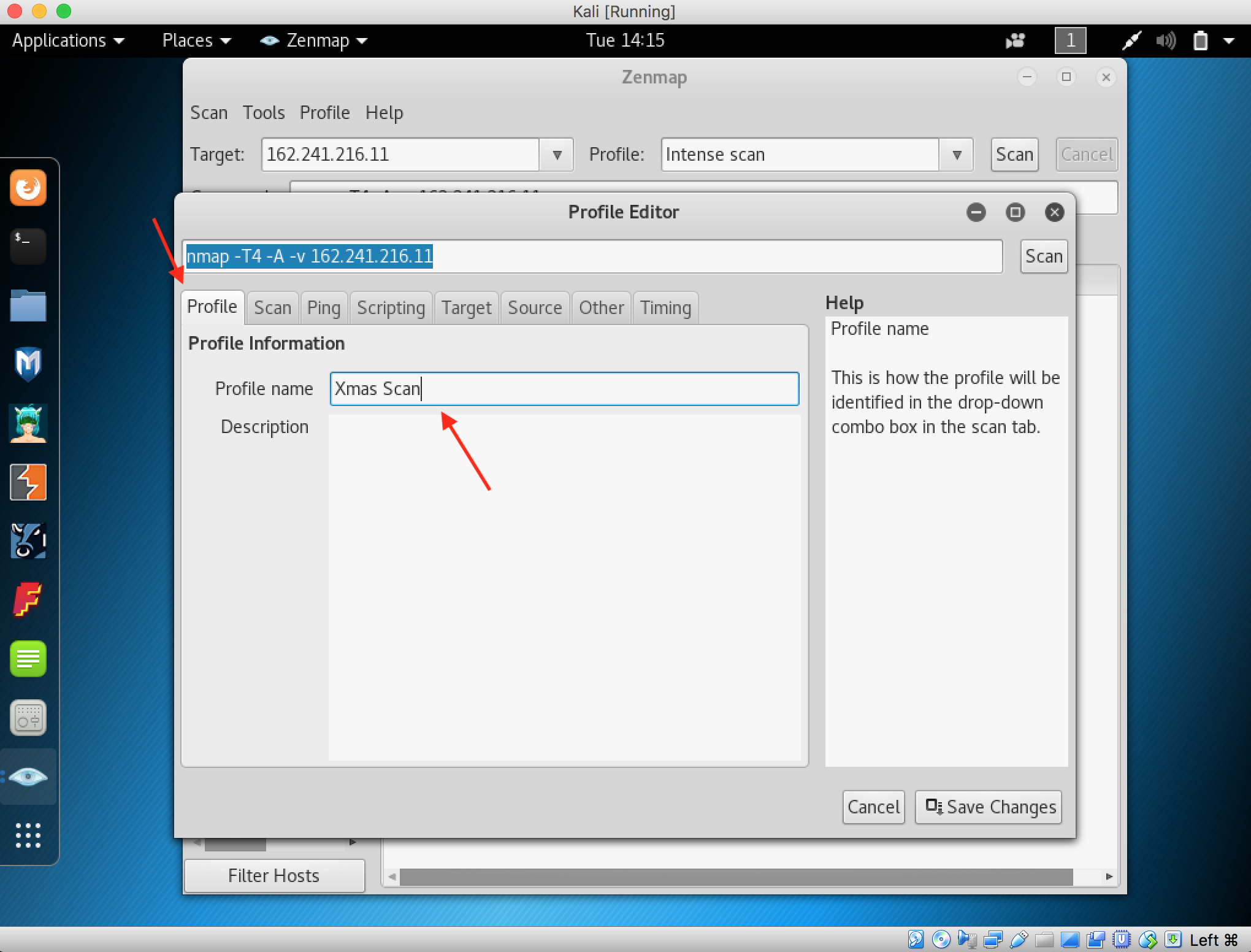
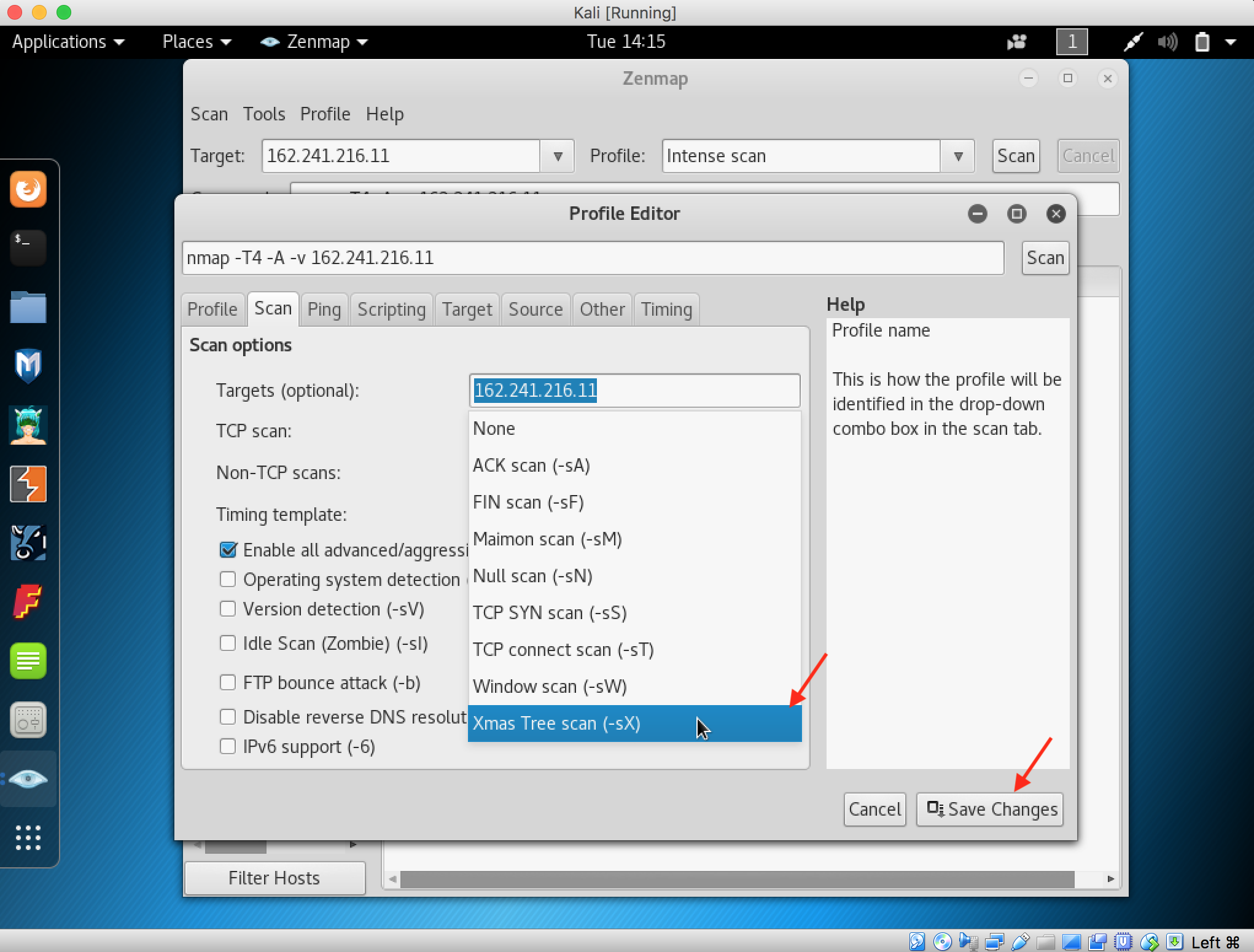
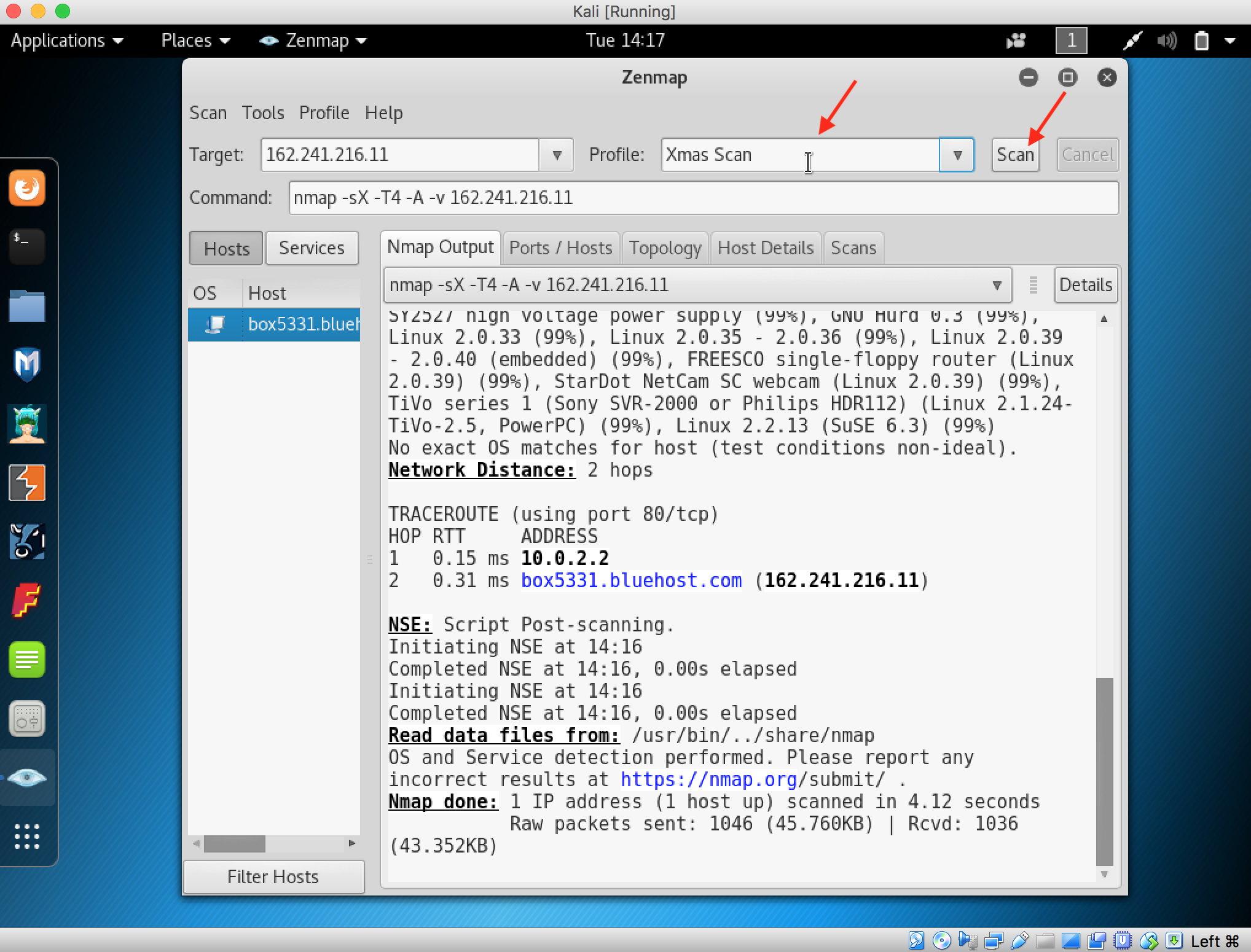
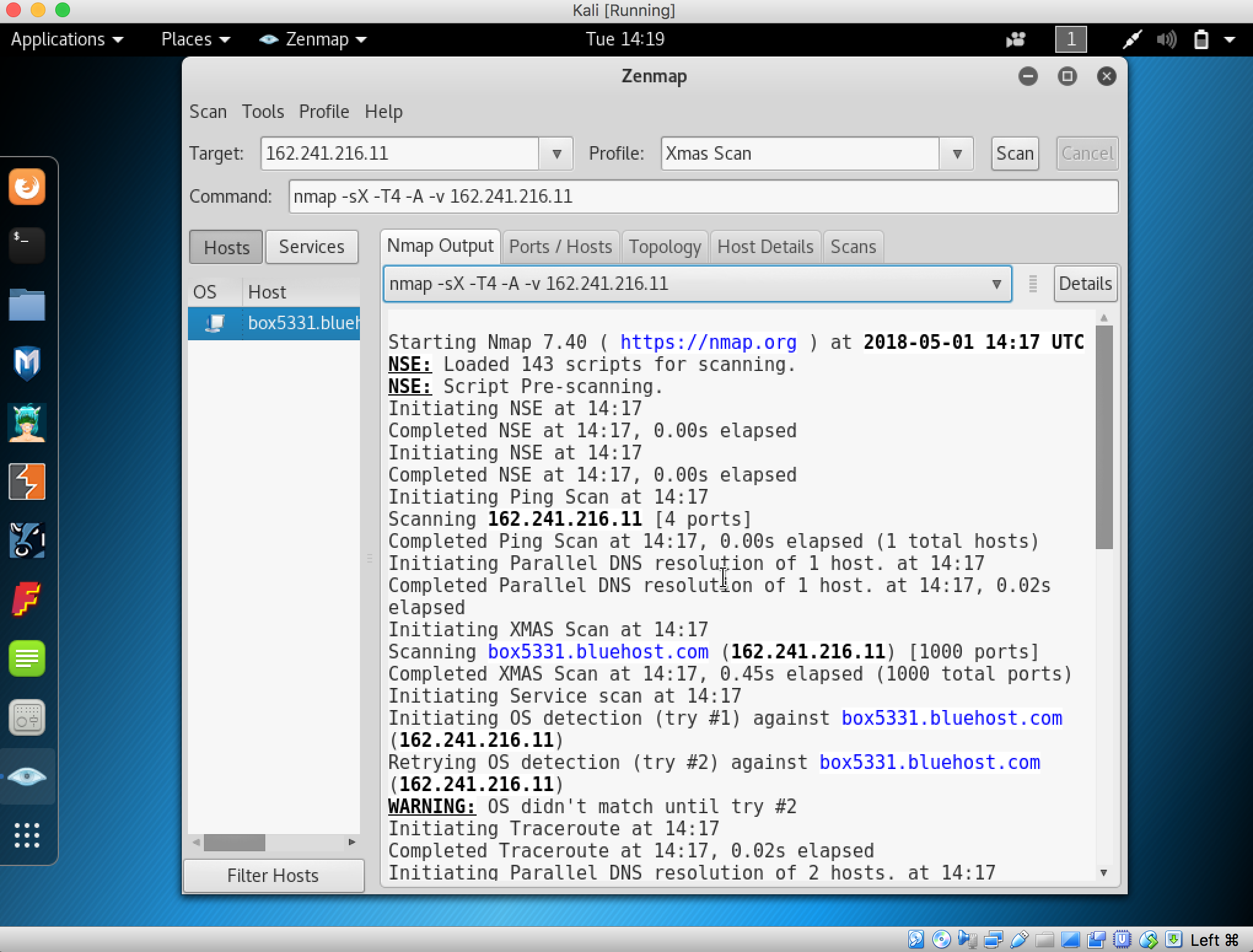
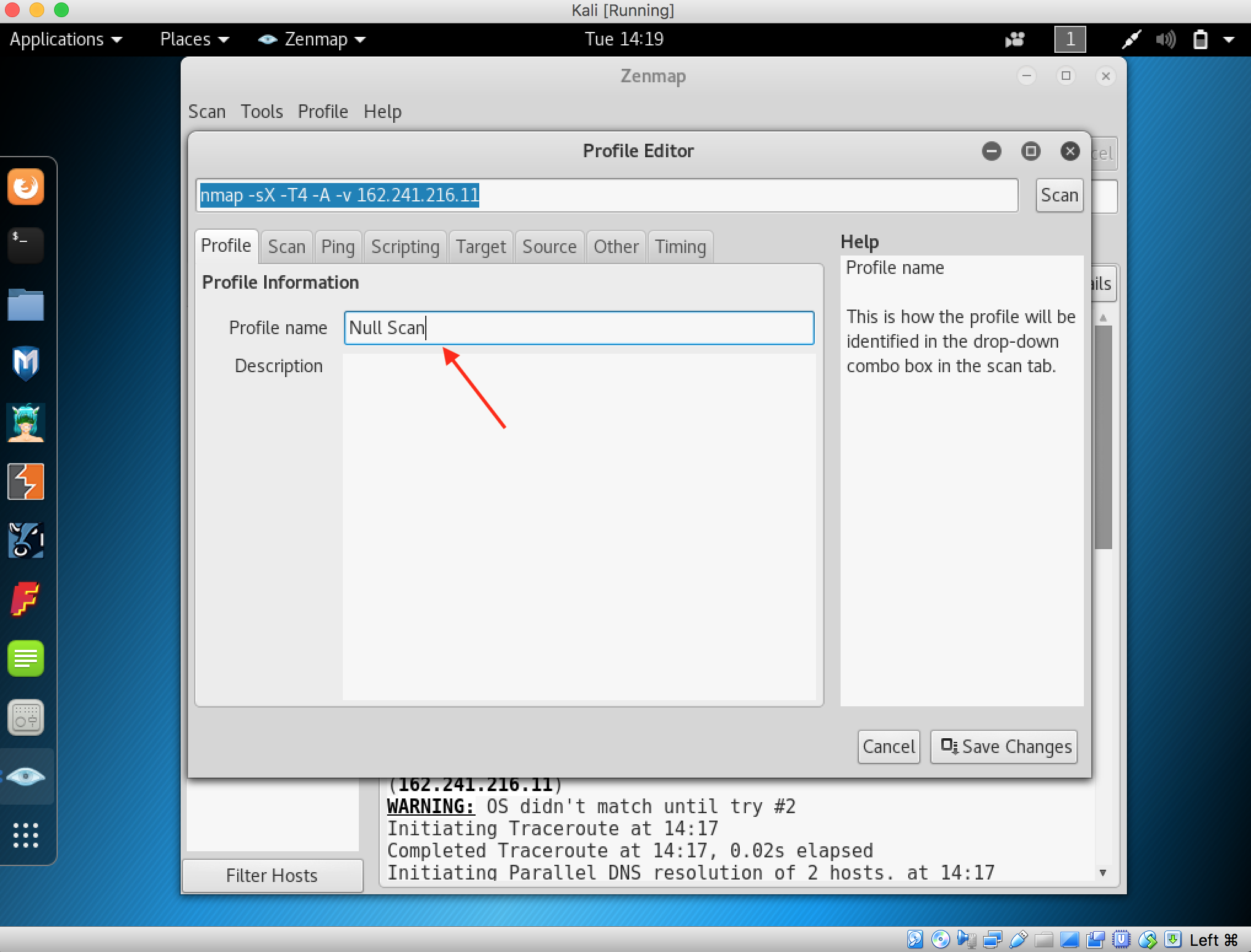
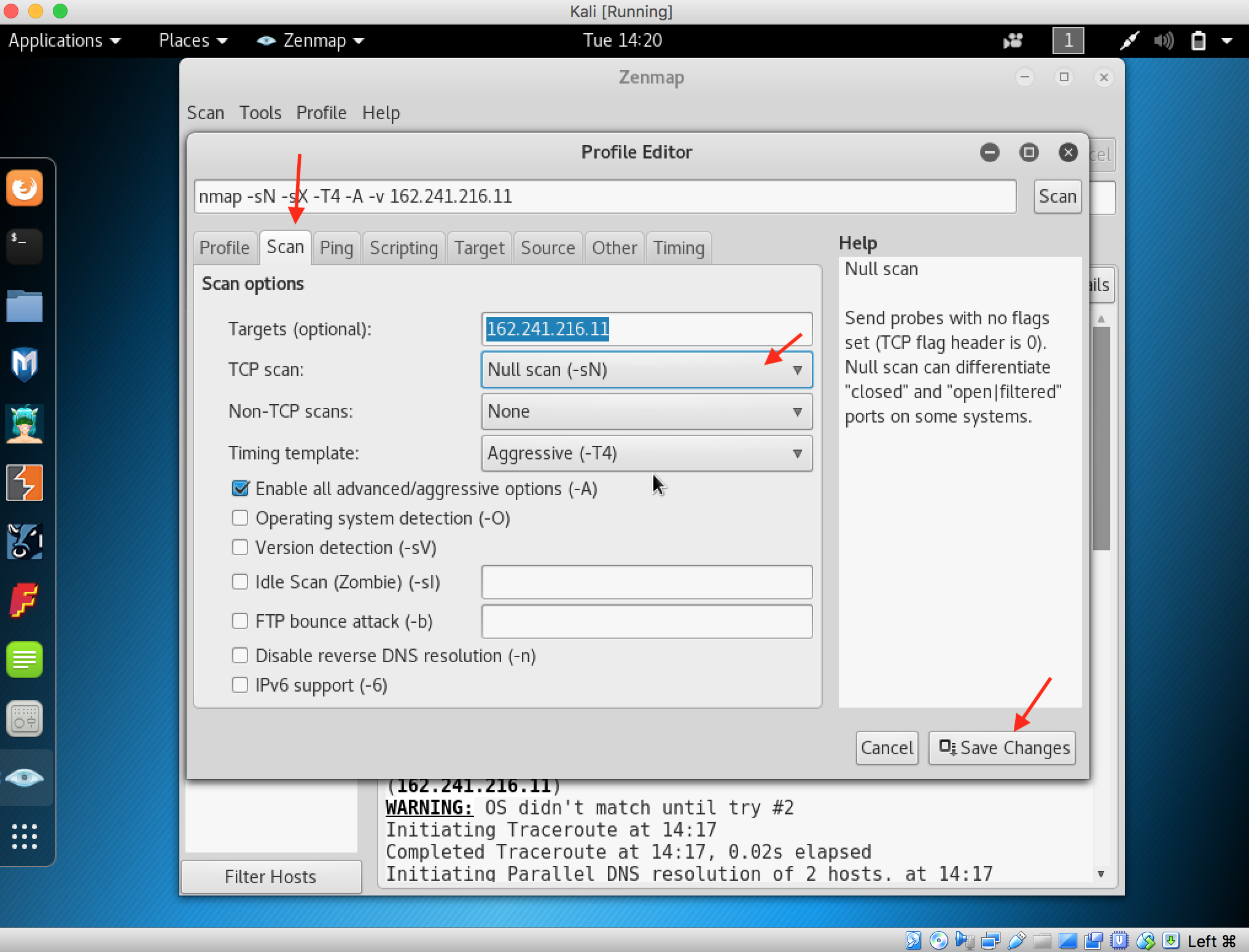
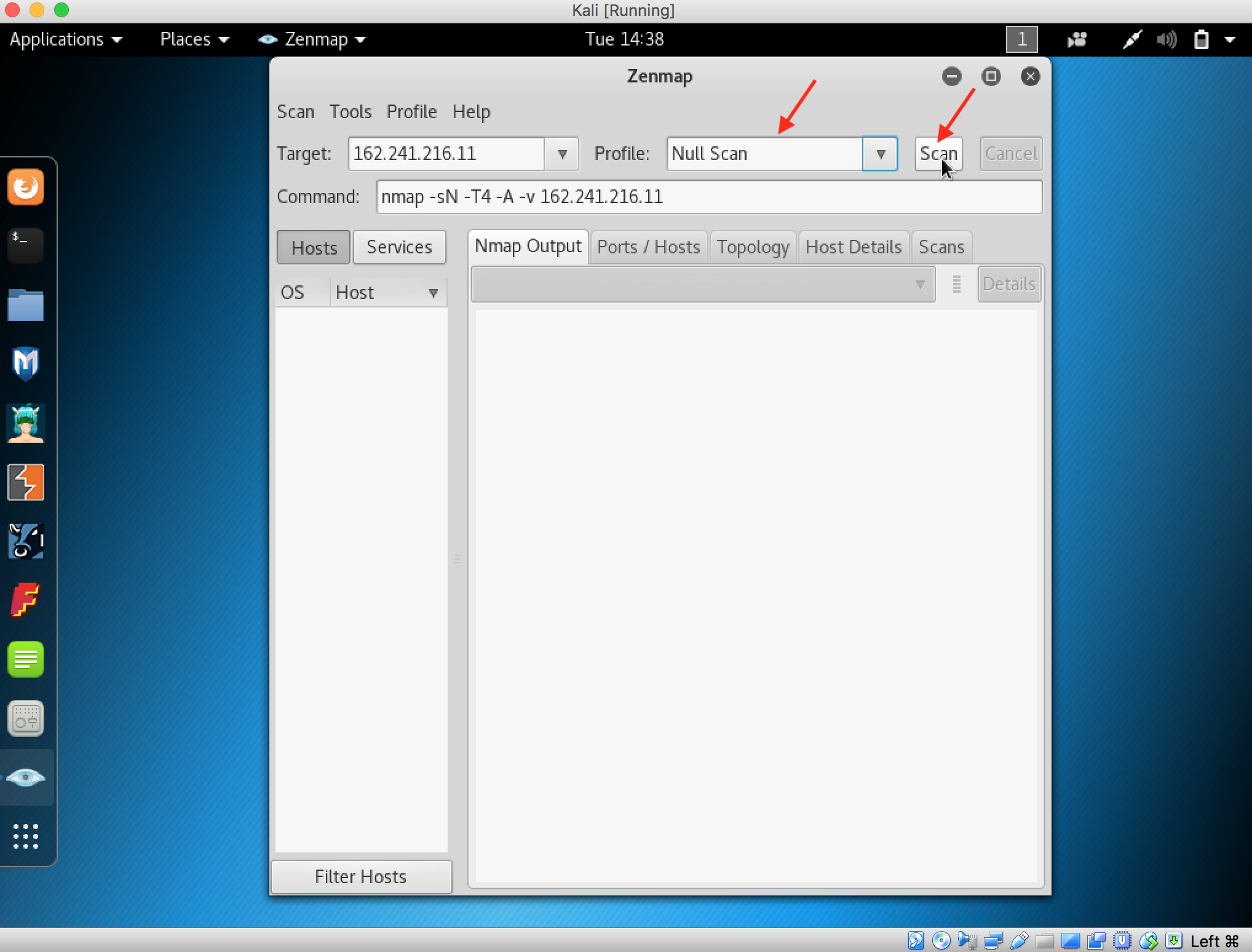
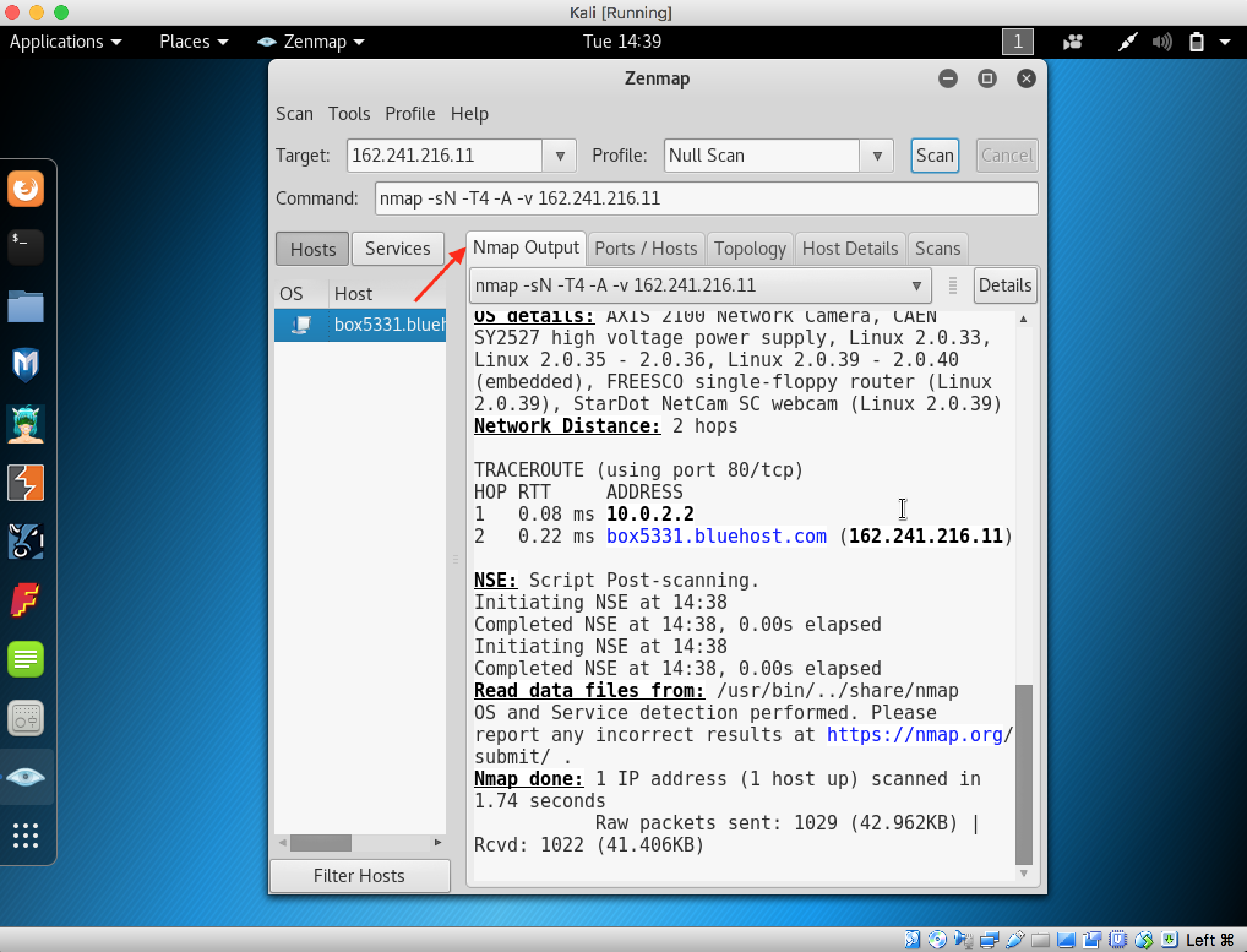
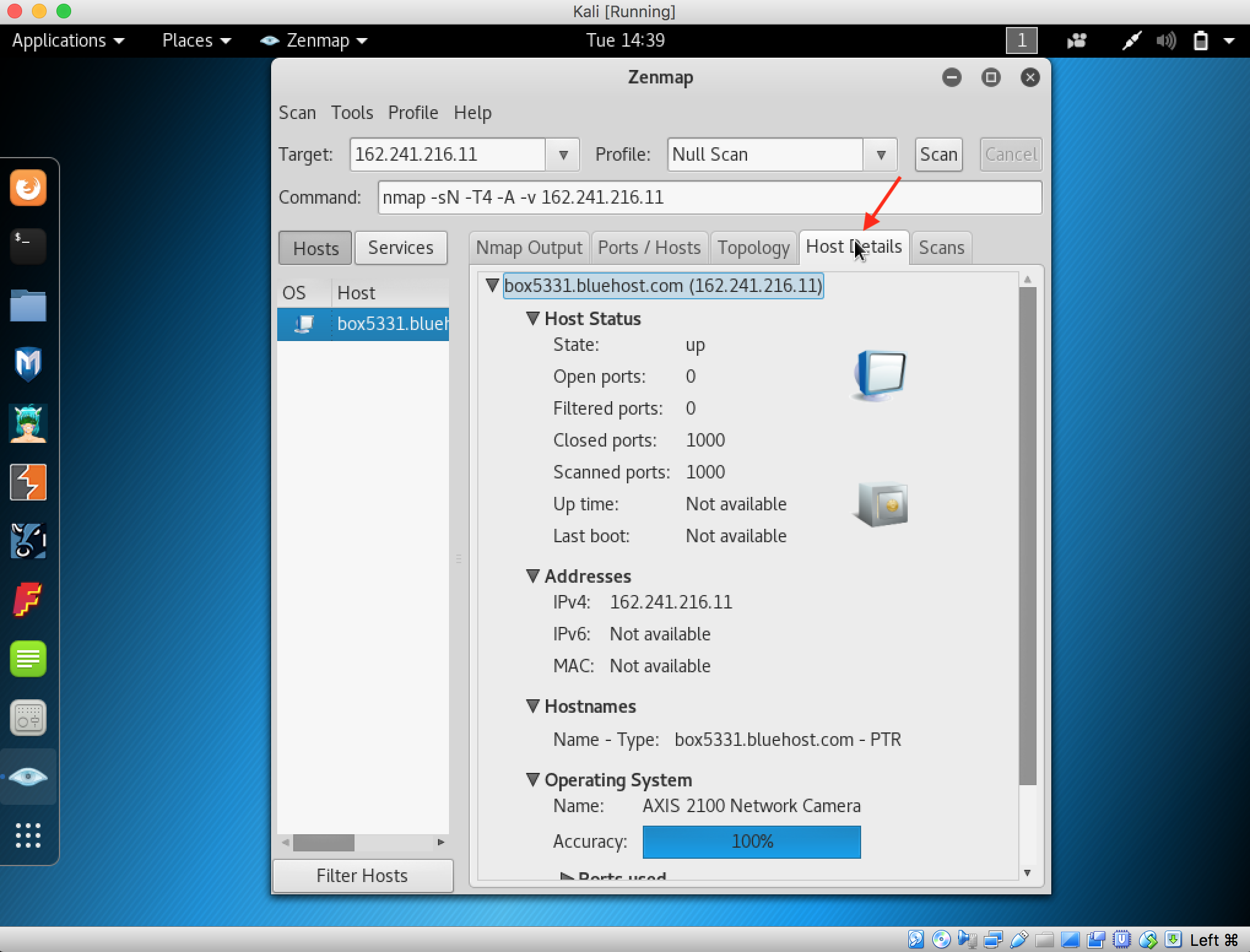
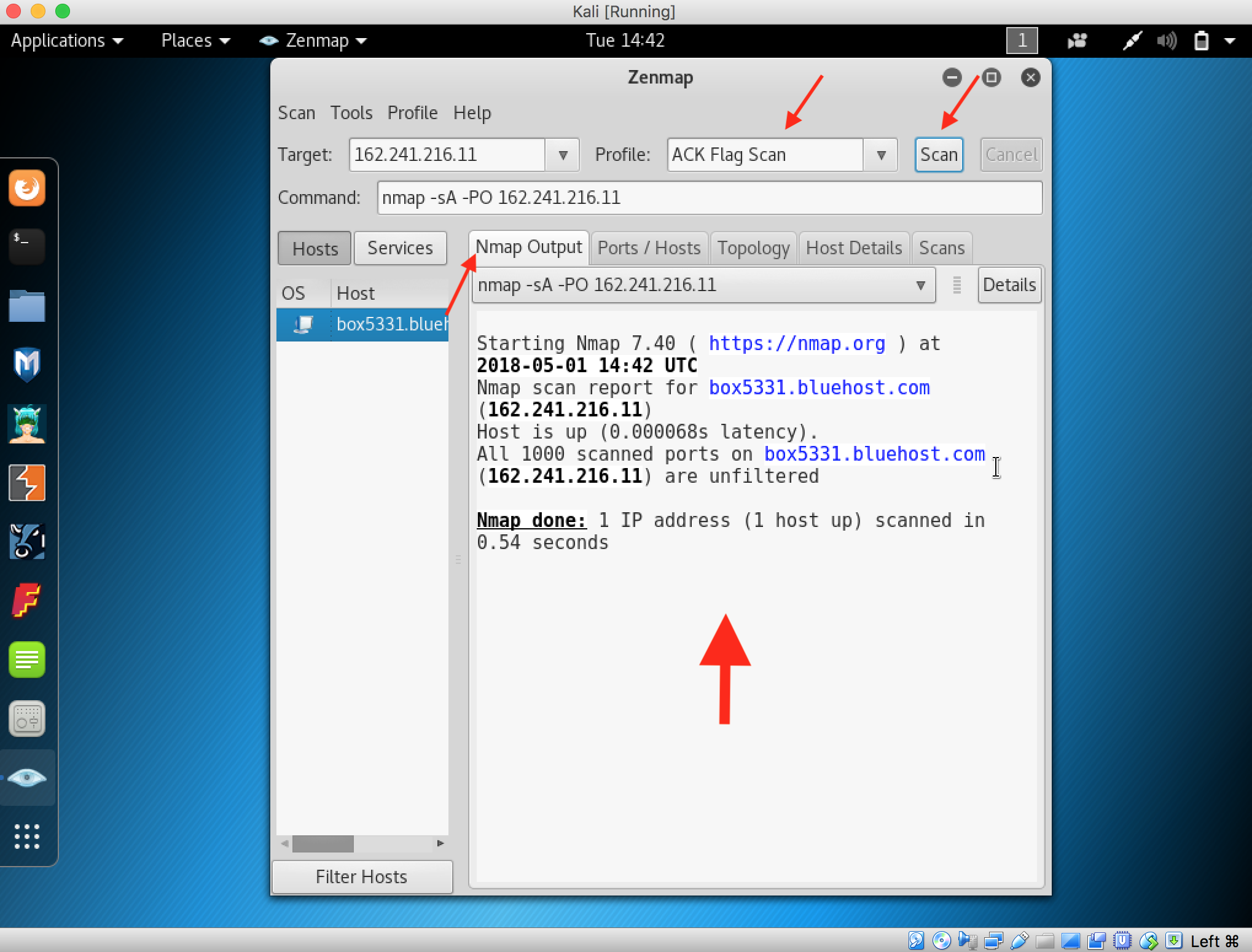
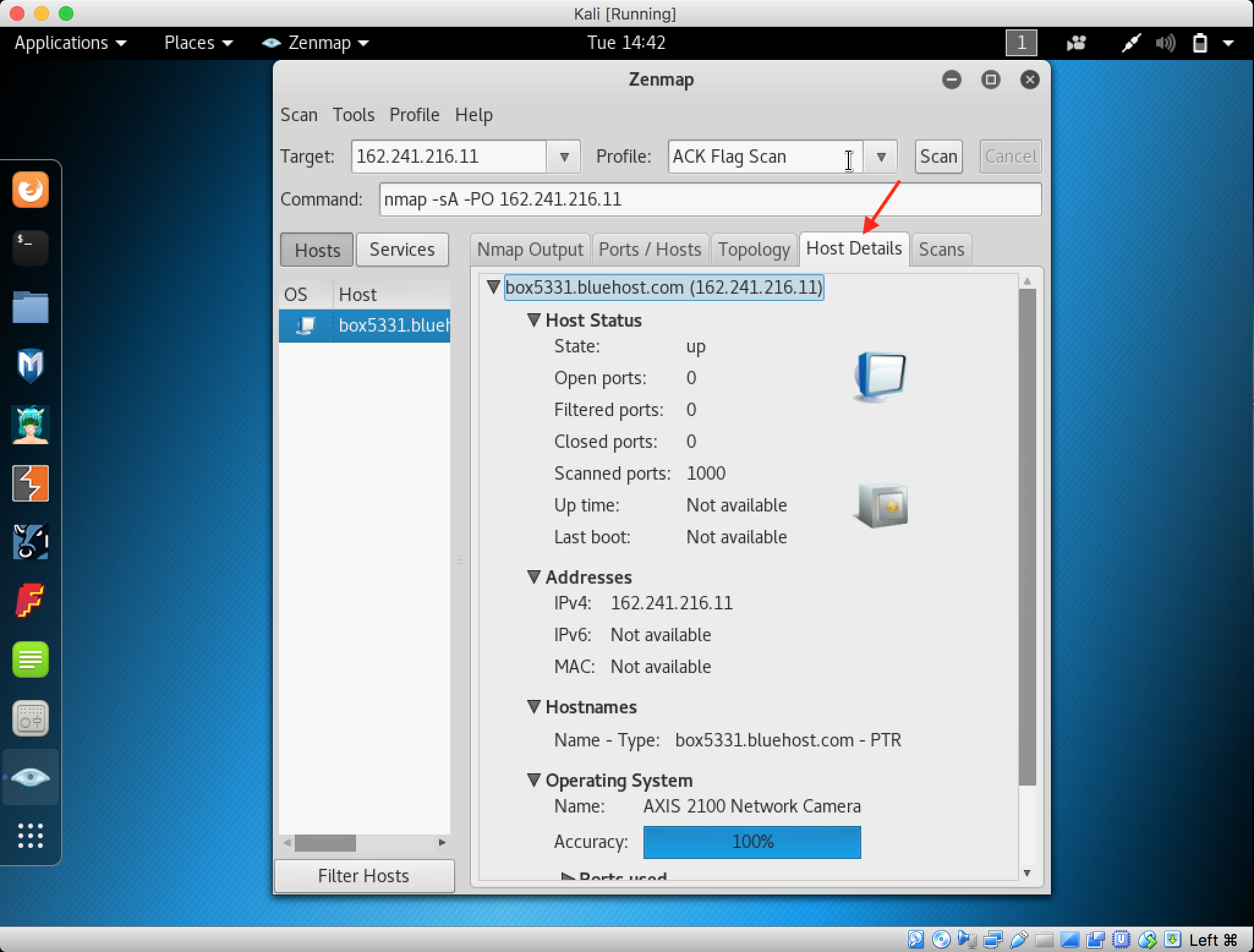
- Launch Hping3 from command terminal by typing hping3 and press enter or through application.
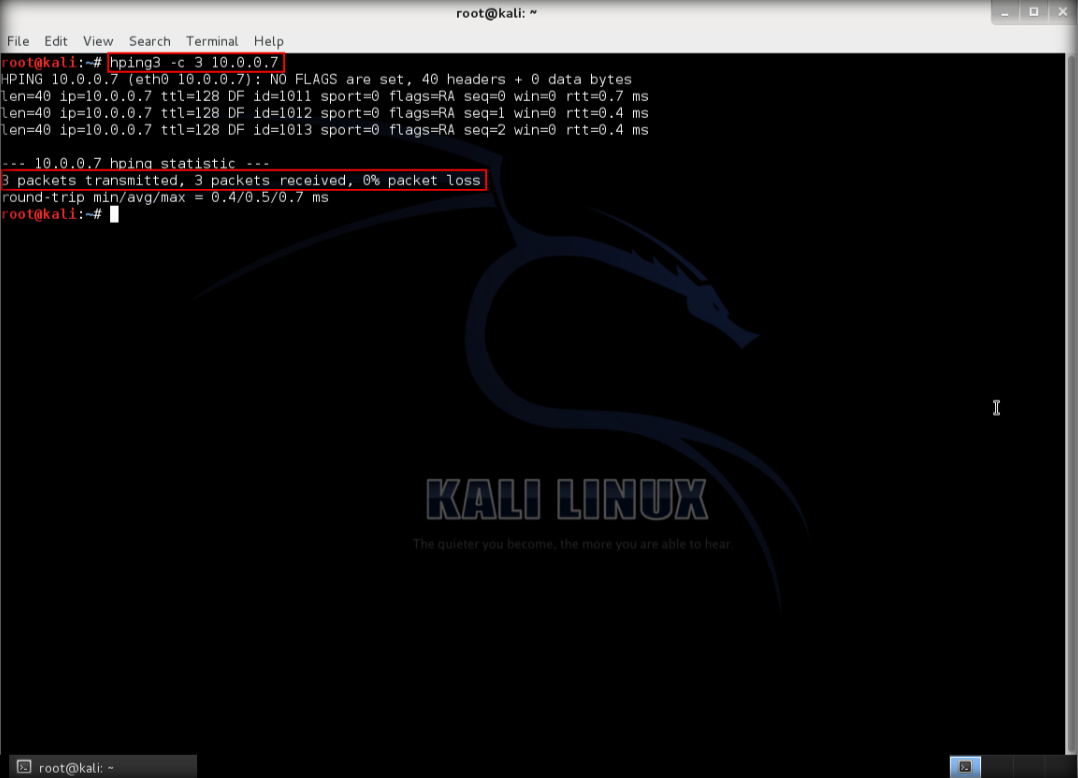
2. After hping3 shows up in the terminal, type hping3 -c 3 <IP address of target machine> then press enter
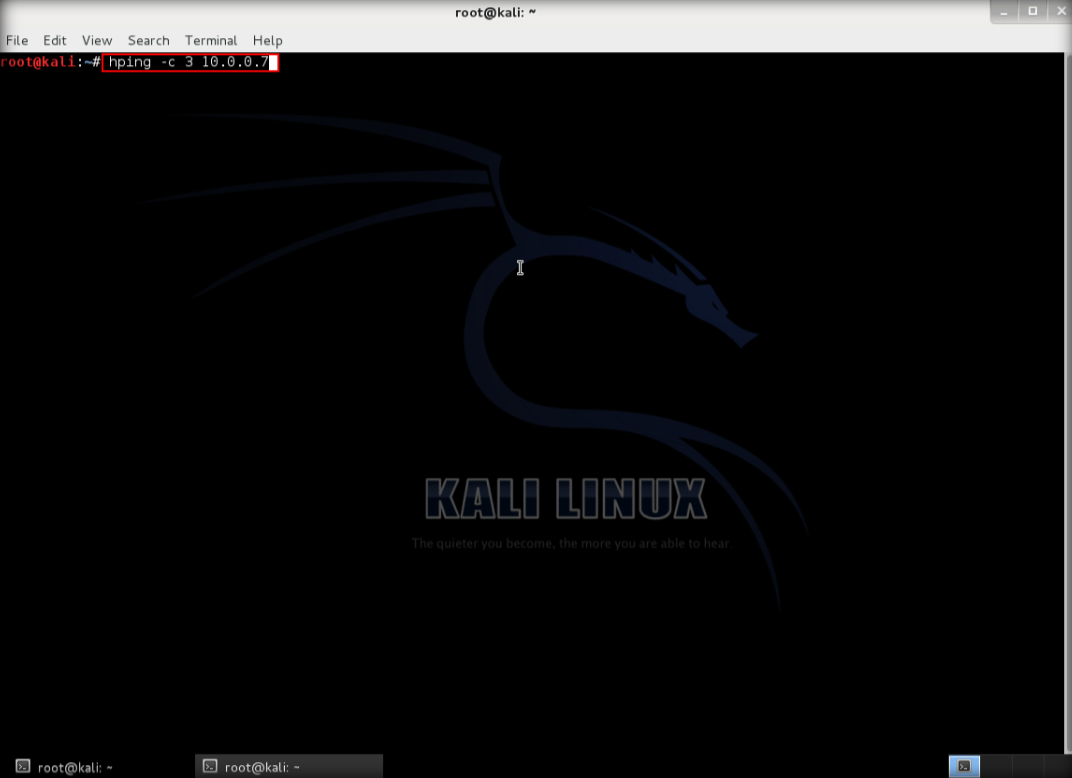
3. After that command, the output will indicate that the packets was received and sent
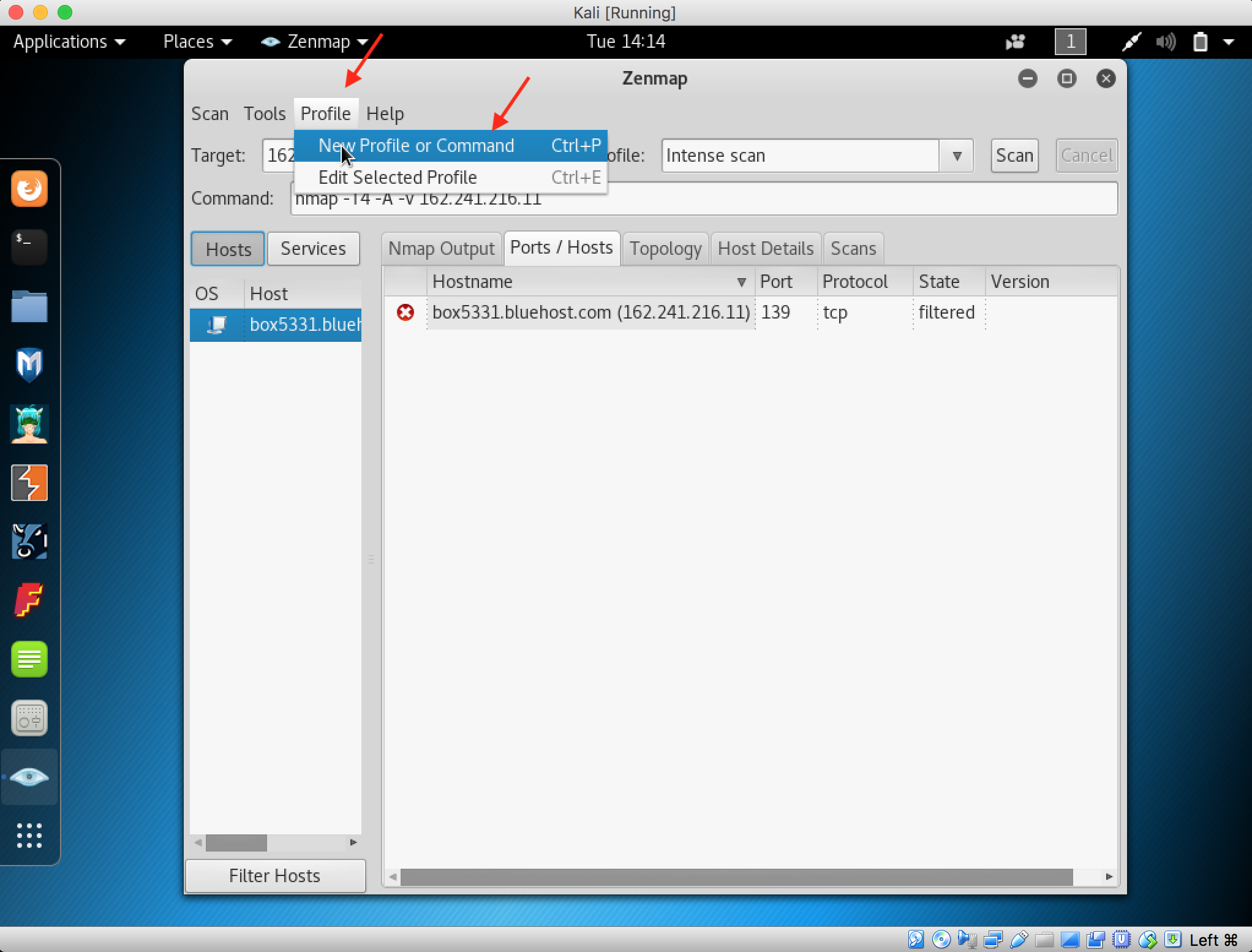
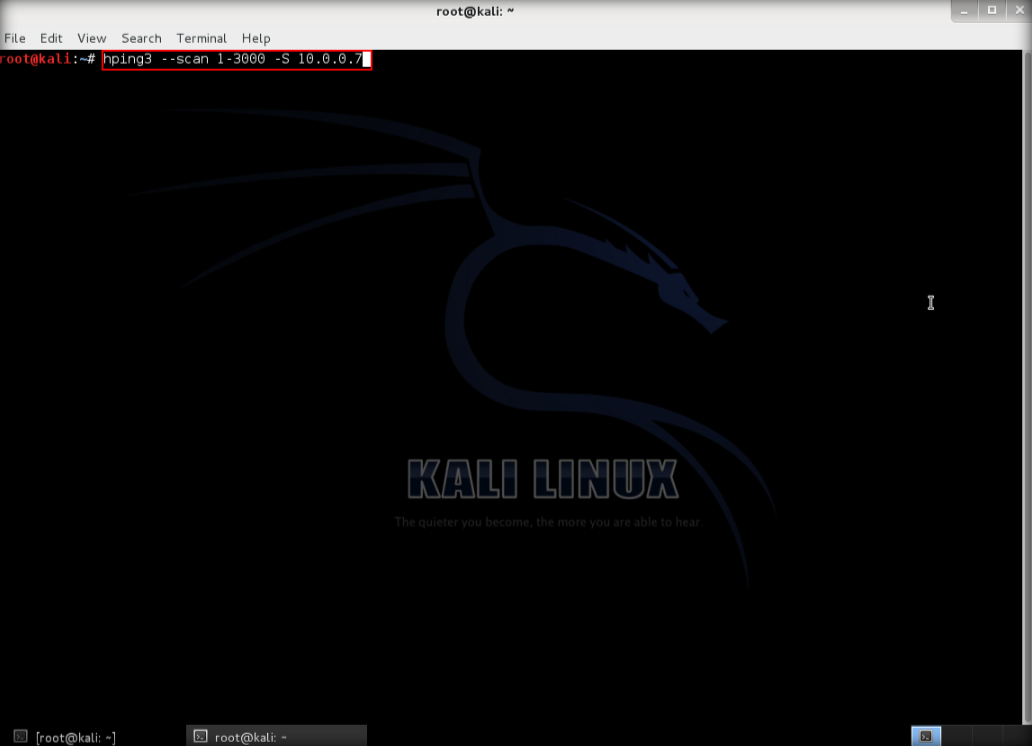
4. Next, type hping3 –scan 1-3000 -S <IP address of target> where –scan defines the port range to scan and -S shows the SYN flag
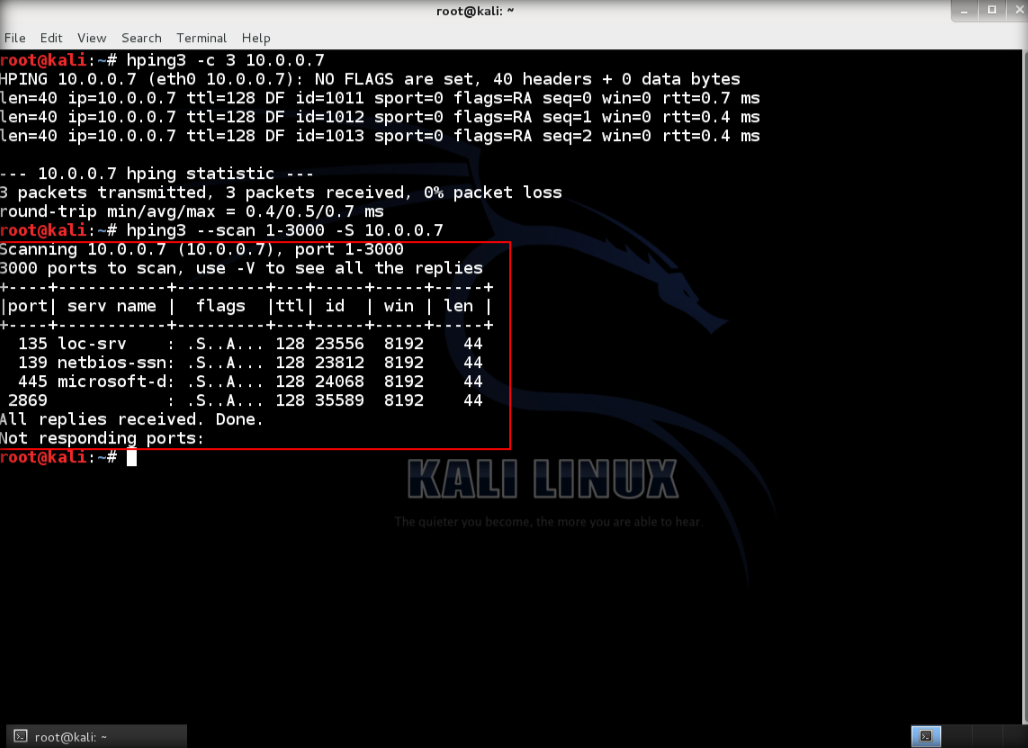
5. The output indicates the open ports from the IP target.
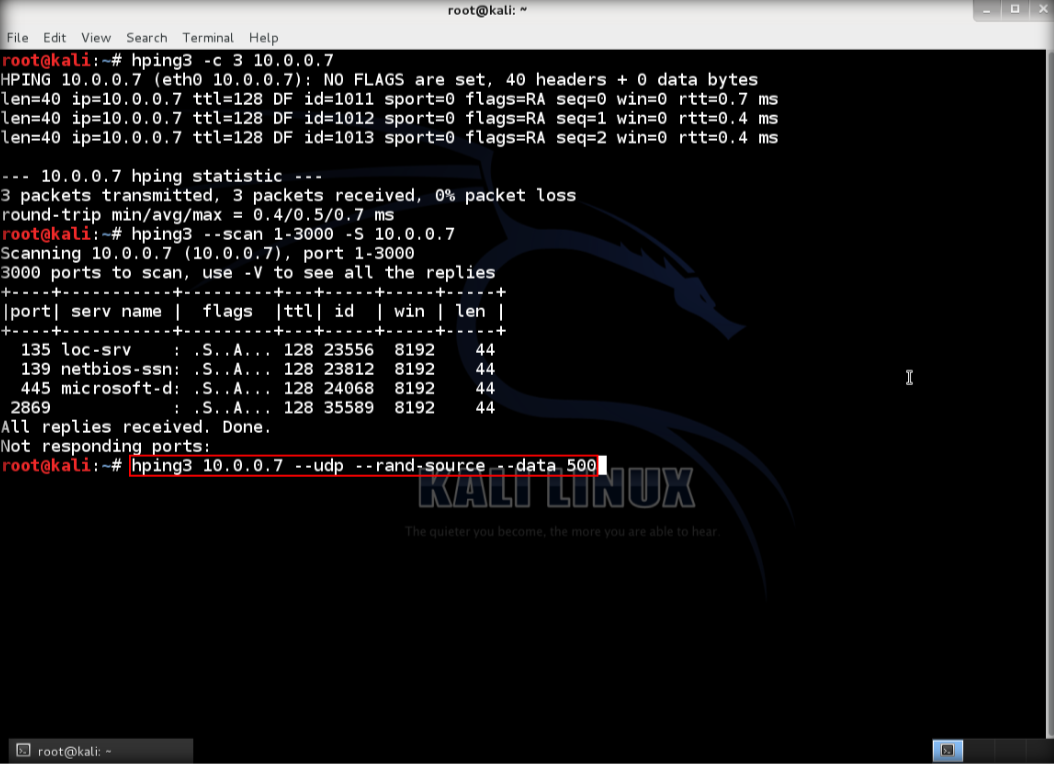
6. Then, use UDP packet crafting, type hping3 <IP address of target> –udp –rand-source –data 500, then enter. This condition, target is running windows 8.1
7. Open the windows 8.1 and launch wireshark to observe UDP packets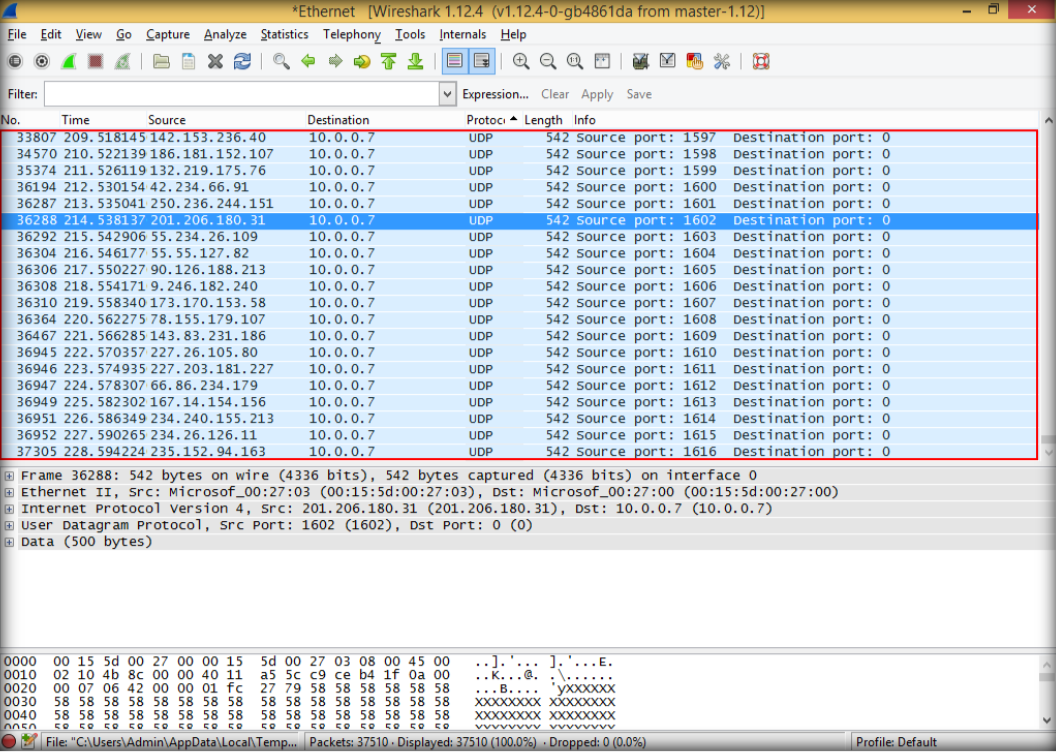
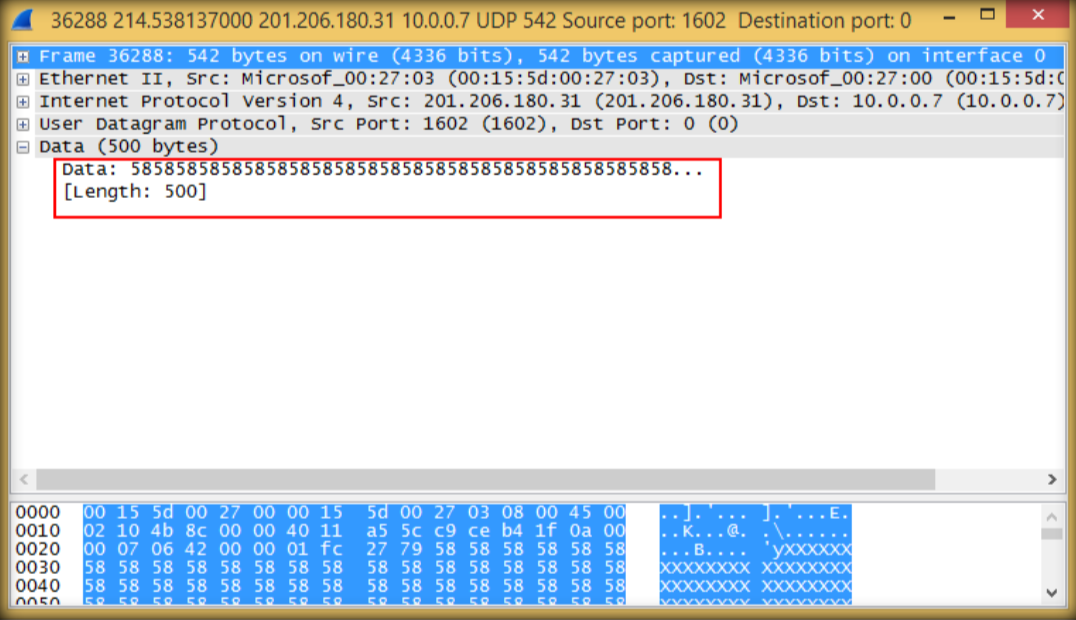
8. Double click to see details, then close wireshark windows and quit without saving.
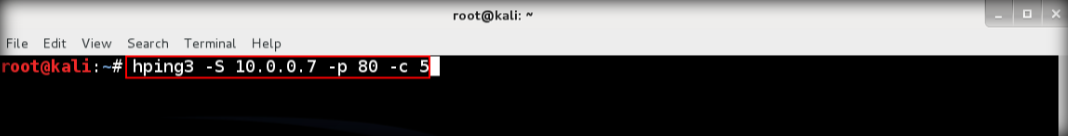
9. Launch wireshark again and leave it running behind, after that send TCP SYN to the target. Type hping3 -S <IP Address of target> -p 80 -c 5 then enter
10. The output shows that TCP packets sent through port 80 to the target
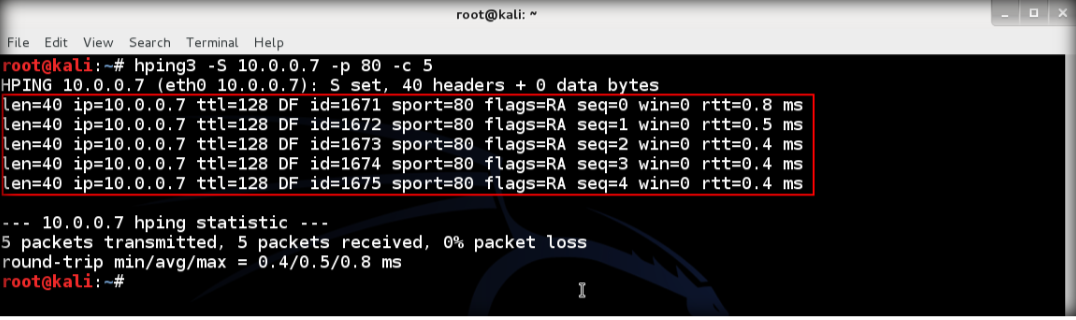
11. Open wireshark again to observe TCP packets captured by wireshark, restart to start new capture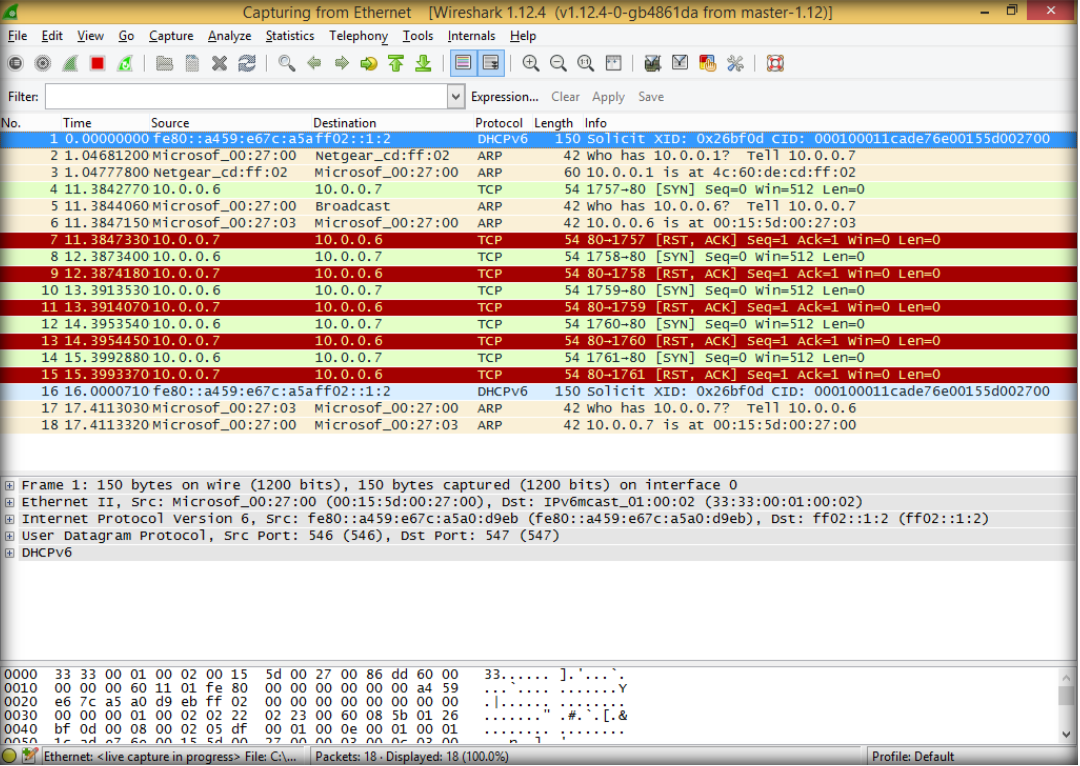
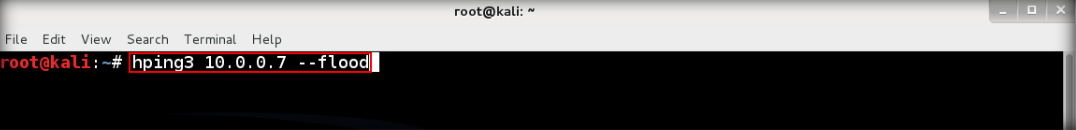
12. Back to Kali again, flood the TCP packets to target. Type hping3 <IP address target> –flood then enter
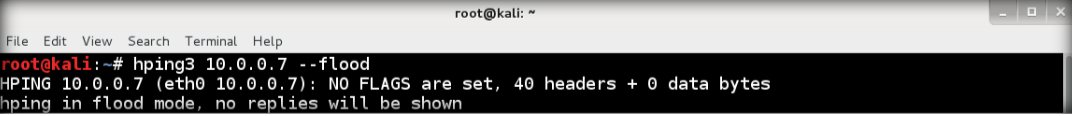
13. After floods to the target, it will respond in terminal
14. Switch back to wireshark, and see how the TCP packets flooding from the attacker
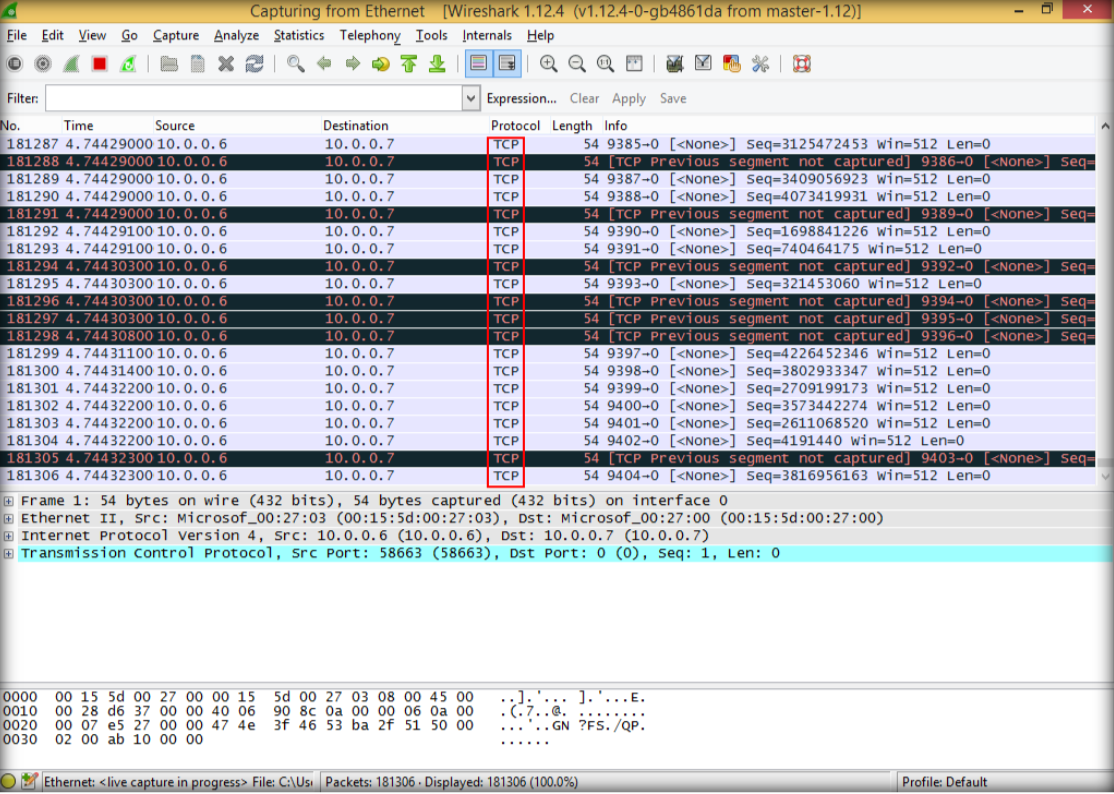
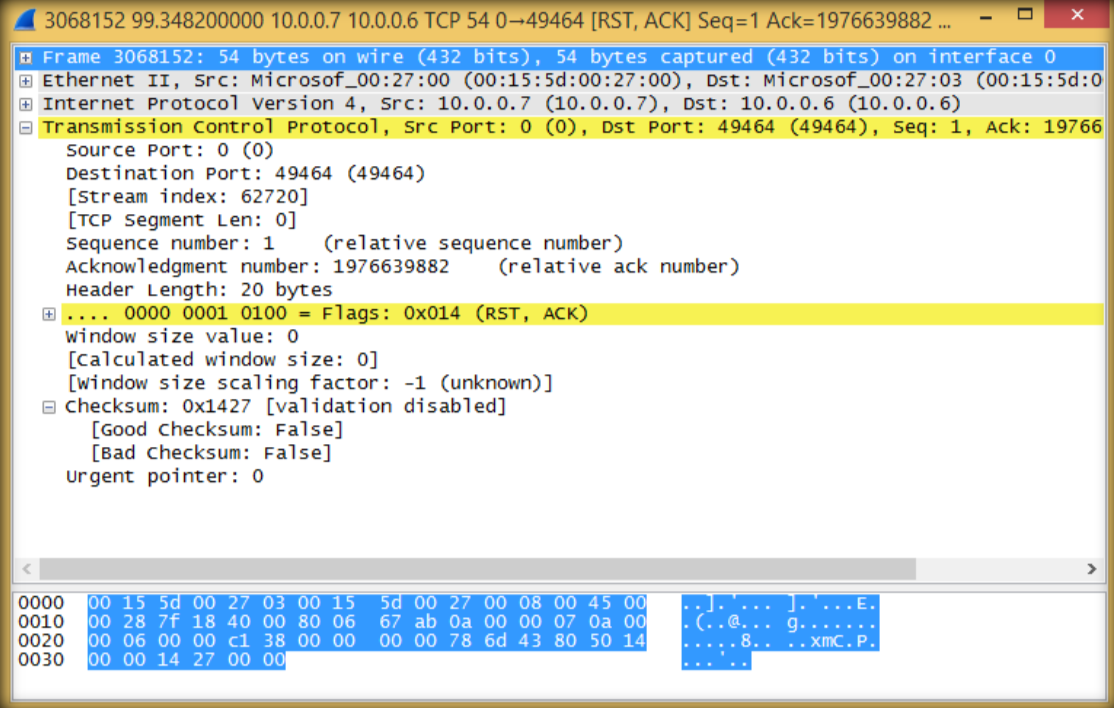
15. Double click to see more detail information regarding TCP packets sent from attacker to target
Posted by :
Bonfilio Aldrino Sugiarto – CS2020 – 2001611794